Sorting Lower Bound
Comparison-Based Sorting
- Many sorting algorithms are comparison based.
- They sort by making comparisons between pairs of objects
- Examples: bubble-sort, selection-sort, insertion-sort, heap-sort, merge-sort, quick-sort, ...
- Let us therefore derive a lower bound on the running time of any algorithm that uses comparisons to sort n elements, x1, x2, …, xn.
Counting Comparisons
- Let us just count comparisons then.
- Each possible run of the algorithm corresponds to a root-to-leaf path in a decision tree
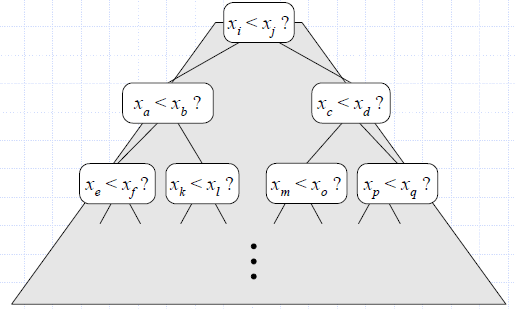
Decision Tree Height
- The height of this decision tree is a lower bound on the running time
- Every possible input permutation must lead to a separate leaf output.
- If not, some input …4…5… would have same output ordering as …5…4…, which would be wrong.
- Since thermein aimruem n h!e=igh1t *(t2im*e…) *n leaves, the height is at least log (n!)
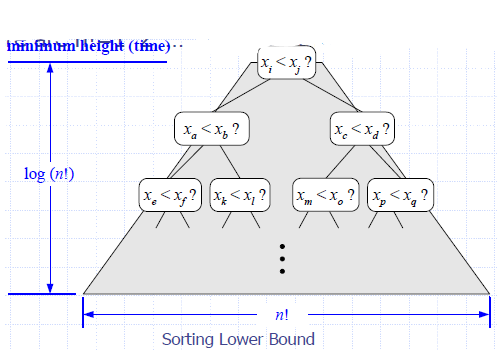
The Lower Bound
- Any comparison-based sorting algorithms takes at least log (n!) time
- Therefore, any such algorithm takes time at least
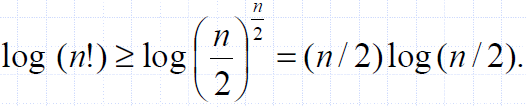
- That is, any comparison-based sorting algorithm must run in Ω(n log n) time.
Code
package examples;
import java.lang.management.ManagementFactory;
import java.lang.management.ThreadMXBean;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
public class SortTest {
public static long cnt;
static Random rand = new Random();
static int [] b;
public static boolean sortCheck(int[] a) {
for (int i=0;i<a.length-1;i++){
if (a[i]>a[i+1]) return false;
}
return true;
}
private static void mSort(int[] a, int from, int to) {
if (from == to) return;
int mid = (from+to)/2;
mSort(a,from,mid);
mSort(a,mid+1,to);
merge(a,from,mid,to);
}
public static void quickSelect(int [] a , int rank){
qSelect(a,0, a.length-1,rank);
}
private static void qSelect(int[] a, int from, int to, int rank) {
int piv = partition(a,from, to);
if (piv==rank) return;
if (rank > piv) qSelect(a,piv+1,to,rank);
else qSelect(a,from,piv-1,rank);
}
public static void bubbleSort(int[] a) {
cnt=0;
int m = a.length-1;
for(int i=m; i>0; i--){
for (int k=0; k < i; k++){
if(a[k]>a[k+1]) swap(a,k,k+1);
}
}
}
static void swap(int [] a, int i, int k){
int tmp=a[i];
a[i]=a[k];
a[k]=tmp;
cnt++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long t1=0,t2=0,te1=0,te2=0,eTime=0,time=0;
int n = 50000000;
Random rand=new Random(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
ThreadMXBean threadBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean();
int [] a = new int[n];
for (int i=0;i<a.length ;i++) {
a[i]=rand.nextInt(n);
}
for (int i=0;i<a.length ;i++) {
swap(a,i,rand.nextInt(n-1));
}
cnt=0;
te1=System.nanoTime();
t1 = threadBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime();
bubbleSort(a);
te2 = System.nanoTime();
t2 = threadBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime();
time=t2-t1;
eTime=te2-te1;
System.out.println("# elements: "+n);
System.out.println("CPU-Time usage: "+time/1000000.0+" ms");
System.out.println("elapsed time: "+eTime/1e6+" ms");
System.out.println("sorted? "+sortCheck(a));
System.out.println("swap operation needed: "+cnt);
}
}