Sets
Set Operations
- We represent a set by the sorted sequence of its elements
- By specializing the auxliliary methods he generic merge algorithm can be used to perform basic set operations:
- union
- intersection
- subtraction
- The running time of an operation on sets A and B should be at most O(nA + nB)
- Set union:
- aIsLess(a, S)
- bIsLess(b, S)
- bothAreEqual(a, b, S)
- Set intersection:
- aIsLess(a, S)
- bIsLess(b, S)
- bothAreEqual(a, b, S)
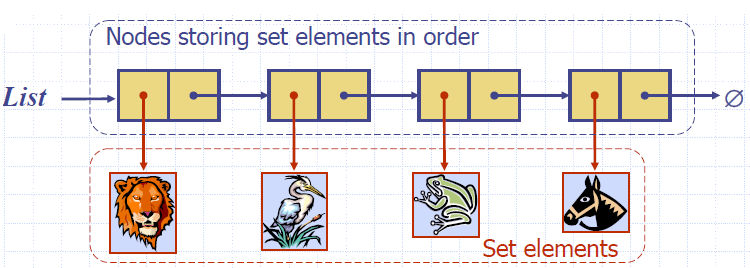
Storing a Set in a List
- We can implement a set with a list
- Elements are stored sorted according to some canonical ordering
- The space used is O(n)
Generic Merging
- Generalized merge of two sorted lists A and B
- Template method genericMerge
- Auxiliary methods
- aIsLess
- bIsLess
- bothAreEqual
- Runs in O(nA + nB) time provided the auxiliary methods run in O(1) time
Algorithm genericMerge(A, B)
S ← empty sequence
while ¬A.isEmpty() ∧ ¬B.isEmpty()
a ← A.first().element(); b ← B.first().element()
if a < b
aIsLess(a, S); A.remove(A.first())
else if b < a
bIsLess(b, S); B.remove(B.first())
else { b = a }
bothAreEqual(a, b, S)
A.remove(A.first()); B.remove(B.first())
while ¬A.isEmpty()
aIsLess(a, S); A.remove(A.first())
while ¬B.isEmpty()
bIsLess(b, S); B.remove(B.first())
return S
Using Generic Merge for Set Operations
- Any of the set operations can be implemented using a generic merge
- For example:
- For intersection: only copy elements that are duplicated in both list
- For union: copy every element from both lists except for the duplicates
- All methods run in linear time.